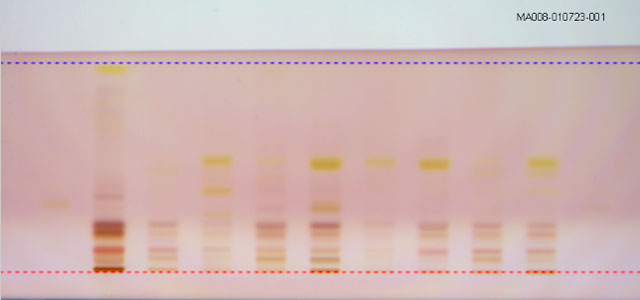
Tamilnadu Test House offers HPTLC Testing services in the below areas for identification and Quantification of the components. HPTLC is a sophisticated instrument which is used for comparing several samples in parallel, checking for adulteration, Purity analysis, and quantifying marker compounds.

Ayush Testing
- Botanical industry for fingerprinting, Identification and quantification of marker compounds, adulterant and falsification.
- Pharmaceutical applications for identification and impurity test.
- Food and cosmetic industry – Aflatoxins, Lipids, Carbohydrates, Food Colors, pigments, other additives
- Environmental analysis – Pesticides, PAH’s
- Forensics / toxicology
Herbal Drugs
- HPTLC fingerprinting of herbal drugs used in gemmotherapy
- Rapid chemotaxonomic discrimination of Clerodendrum species
- Analysis of innovative plant extracts
- Pharmacokinetics of berberine from Pushyanuga Churna
- Simplified analysis of purity of ginkgo products
- HPTLC-UV fingerprints of Gelsemium elegans and koumine contents determined by densitometry compared to UPLC-MS/MS
- Comprehensive HPTLC fingerprinting for the quality control of Angelica gigas root
- Qualitative and quantitative HPTLC analysis of licorice root
- Comparison of conventional TLC and HPTLC for identity testing of herbal medicinal extracts
- Adulteration of St. John’s Wort Products (Herbal Medicine Manufacturer)
- The unique merits of HPTLC image analysis for quality control of herbal medicines
- Marker compounds in Java tea characterized by HPTLC
- Screening of three PDE5-Inhibitors and eight of their analogs in lifestyle products
- Bioassay-guided isolation of plant antibiotics
- Quantification of alkaloids in Sceletium tortuosum
- Identification of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors from Galbanum
- Planar-chromatographic fingerprint of German propolis
- Rapid structure confirmation and quantitation by HPTLC-NMR
- Bioautographic HPTLC assays for screening of Gabonese medicinal plants used against Diabetes mellitus
- Identification of polyphenolic compounds in Rheum officinale Baill. by TLC-MS-coupling
- Simultaneous analysis of temephos and fenitrothion in green tea
- TLC/HPTLC fingerprinting of herbal essential oil followed by liquid chromatography hyphenated with the TLC-MS Interface
- Quality control of Traditional Chinese Medicines by HPTLC
- Separation of common plant triterpenoids by HPTLC
- A comparison between HPLC and HPTLC for the separation and quantification of boswellic acids in Boswellia serrata extracts
- Screening of unknown plant extracts by planar chromatography
- HPTLC-identification of Hoodia gordonii, a popular ingredient of botanical slimming products
- Validation of HPTLC methods for the identification of botanicals
Food
- Characterization of E472 food emulsifiers by HPTLC fingerprints
- Comparison of yeast estrogen screening on HPTLC and in microtiter plates
- Analysis of neonicotinoids in honey by complementary use of Planar Chromatography – HPLC and Mass Spectrometry
- Screening of weight loss products for deliberately added undeclared synthetic drugs
- Lovastatin and citrinin in red yeast rice products
- Screening of steroids as adulterants in food supplements
- Fast determination of benzoic acid in food
- Fast determination of benzoic acid in food
- HPTLC quantification of cocoa ingredients and their changes during different chocolate manufacturing steps
- Quantification of Bitter Acids in Hops
- Quantification of steviol glycosides and steviol/isosteviol
- Screening for ricinoleic acid as marker for Secale cornutum impurities in rye
- Rapid screening for ergot alkaloids in rye flour by planar solid phase extraction (pSPE)
- Quantification of wax ester content in escolar
- Determination of the hemolytic activity of saponins by an HPTLCblood gelatin test
- Identification of herbal slimming drugs and screening for adulteration by HPTLC
- Determination of lactose in foodstuff
- Modern direct bioautography of endocrine active compounds
- HPTLC-UV/MS of caffeine in energy drinks
- Anthocyanes in food and animal feed by HPTLC-Vis-(EDA-)MS
- Solid phase extraction as clean-up for pesticide residue analysis of tea samples using planar chromatographic developing techniques
- Quantitative determination of steviol glycosides (Stevia sweetener)
- TLC screening for the detection of Robusta admixtures to Arabica coffee
- The fingerprint of biopolymers (polysaccharides)
- Fast quantification of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in honey
- Planar solid phase extraction – a new clean-up concept in residue analysis of pesticides
- Determination of enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin in milk by direct bioautography detection
- Determination of the glycoalkaloids -solanine and -chaconine in potatoes at different steps of potato processing
- Analysis of water-soluble food dyes
- Determination of unauthorized fat-soluble azo dyes in spices by HPTLC
- HPTLC determination of illegal dyes in chili, paprika und curry
- Quantification of piperine in black pepper fruit (Piper nigrum L.) and test for minimum content (MCT) of piperine (> 3% Ph. Eur.)
- Limit test for adulteration of black pepper fruit (Piper nigrum L.) with papaya seed (Carica papaya L.)
- Identification of Tangerine Peel (Citrus reticulata Blanco)
Biotechnology
- Characterization of the invertase activity and identification of botanical substrates by densitometry and MALDI-TOF MS
- Dextrin profiles of starch digested with different amylases
- Analysis of insulin samples from different species by HPTLC-MS
- Use of Planar Chromatography for the analysis of peptides from tryptic protein digest
Cosmetics
- Screening for natural cosmetic preservatives by HPTLC-EDA
- Validated method for fast quantification of glycine in cosmetics
- AMD analysis and determination of biocides in lens cleaning fluid
- Quality control of cosmetic products by HPTLC
- Quantification of xanthones in mangosteen fruit hull extracts
- HPTLC bioautographic assay for tyrosinase inhibitors in plant extracts
- Screening method to study the reactivity of cosmetic UV filters on skin proteins
- Detection and determination of caffeine, taurine and arginine in shampoos
- Quantification and side component analysis of the cosmetic active tiliroside using planar chromatography
- Determination of aloe vera gel in cosmetics
- HPTLC fingerprint of Edelweiss plants and extracts used as ingredients in cosmeceuticals
- Detection of UV filters in cosmetic products (sunscreen) by HPTLC and confirmation by HPTLC-MS
- HPTLC method for determination of ceramides from human skin
Pharmaceutical
- TLC and HPTLC-MS in the manufacturing of clinical API batches
- Degradation profiling of cefixime and azithromycin (antibiotics).
- Cleaning validation at API production units
- Simultaneous determination of pioglitazone, metformine and glimepiride in pharmaceutical preparations
- Rapid test for content uniformity of Coenzyme Q10 in soft gel capsules by HPTLC
- Cleaning validation using HPTLC
- TLC/HPTLC-ELSD-MS coupling
- Validated determination of secoisolariciresinol diglucoside in flaxseed by HPTLC
- Screening for bioactive natural products in sponges
- Use of HPTLC as a problem solving technique in pharmaceutical analysis
- Identification and quantification of amino acids in peptides
- Fast identification of unknown impurities by HPTLC/MS
- Rapid content uniformity test of 6 batches of coenzyme Q10 in soft gel capsules by HPTLC
- Determination of Metronidazole in pharmaceutical dosage form by HPTLC
- Detection of Impurities in Bupropion Hydrochloride by HPTLC
Chemical
- Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in road surfaces
- The CAMAG TLC-MS Interface 2 in practice
- Determination of PAHs in toys by HPTLC
- Determination of additives in plastic foils
- Determination of SARA (Saturates, Aromatics, Resins and Asphaltenes) in bitumen by HPTLC
Environmental
- Evolution of plant defense compounds in the plantlitter continuum
- Effect-directed analysis with HPTLC for water and environmental samples
- Effect-directed analysis of a water sample
- New screening concept for pesticide residue analysis in fruit and vegetables – HTpSPE-HRMS
- HPTLC-MS combined with H/D exchange for the identification of substances in environmental analysis
- Effect-directed analysis of environmental samples
- Drinking water treatment – Identification of reaction by-products of 4- and 5-methyl1H-benzotriazole formed during ozonation
- HPLC-MS or simply HPTLC for analysis of sucralose in water?
- 1H-Benzotriazole and tolyl triazole in the aquatic environment
Other
- Characterization of the invertase activity and identification of botanical substrates by densitometry and MALDI-TOF MS
- HPTLC-based effect-directed workflow in drug discovery
- Optimized HPTLC-MS method for identification of constituents in broad-leaved dock
- Comparison of different derivatization techniques
- HPTLC for the quantitation of nicotine in liquids for electronic cigarettes
- CAMAG Derivatizer – New spraying device for the automated derivatization of TLC plates
- Quantification of nicotine in liquids for electronic cigarettes
- Vision CATS 2.0 – Our new software for qualitative and quantitative HPTLC analysis
- Analysis of plant glycosylceramides by automated multiple development
- Introducing the new generation software – visionCATS
- Introduction of special HPTLC and TLC plates for coupling with mass spectrometry
- HPTLC-MS analysis using a novel compact single quadrupole mass spectrometer
- Optimization of an AMD2 method for determination of stratum corneum lipids
- Validated HPTLC method for skin lipids
- The new TLC-MS Interface
- Use of reversed phase (RP)-modified pre-coated plates